Remote Management of Foreign Customers
New ICT technologies allow Small or Medium-sized enterprises to put the customer at the centre of their business activities
Pubblicato da Valerio Ronci. .
SME Planning International marketing Internationalisation Foreign markets Digital Export
Remote management of foreign customers is one of the activities that is benefiting most from new digital technologies. This activity should be considered as a support to the traditional offline management of current and potential customers, and not as a substitute activity.
Human interactions are still a key element for building relationships and selling.
A powerful tool for remote management of foreign customers is the Customer Relationship Management system (CRM). CRM helps to relate with foreign customers in an effective and timely way, allowing to keep track of all conversations between the company and the customer. A correct implementation of a CRM system implies, first of all, a strategic choice on the part of the company: putting the customer at the centre of its business activities.
If the company doesn't have a CRM system, it can manage customers remotely and effectively through three good practices:
- Immediate lead registration
- Definition of the outreach sequence
- Maintaining the relationship even after the sale
Immediate lead registration
When a person expresses an interest in a company’s product/service, they become a lead (business contact) and are immediately added in an Excel sheet, or any other software used to register contacts (see the previous article Lead Generation in International Markets).
If the lead is generated online, e.g. by downloading an e-book, the lead automatically enters the business contacts list (if the company has a CRM system).
If the lead is generated offline, e.g. through a business card, the company will have to register the lead manually. The basic contact information is their email address. However, it is advisable that the company also collects name, telephone number and, in the case of a B2B contact, the company’s name.
Definition of the outreach sequence
After the registration of a potential customer's personal data, it is important to define the outreach sequence. This phase aims to build a relationship with the potential customer, in order to turn them into a paying customer.
If lead does not answer the phone or email, it is good practice to make 6-7 attempts before quitting.
Note that an outreach attempt does not correspond to a single call (contact attempt). Each call consists of 2-3 attempts, usually made with different media tools. For example:
- Make a call and leave a message
- Send an e-mail
- If the company is already connected with the potential customer on a social media platform, also send a message. If the company is not already connected, send a connection request with an invitation message.
The outreach sequence has two main objectives:
- Turning a stranger into a potential customer
- Obtaining additional information about the lead and understanding if they are qualified to buy (lead qualification)
During the outreach sequence, it is essential for the seller to provide timely relevant answers and business content suitable for the potential customer's purchasing process.
Suppose a 6-step outreach sequence for a company producing food cooking machinery.
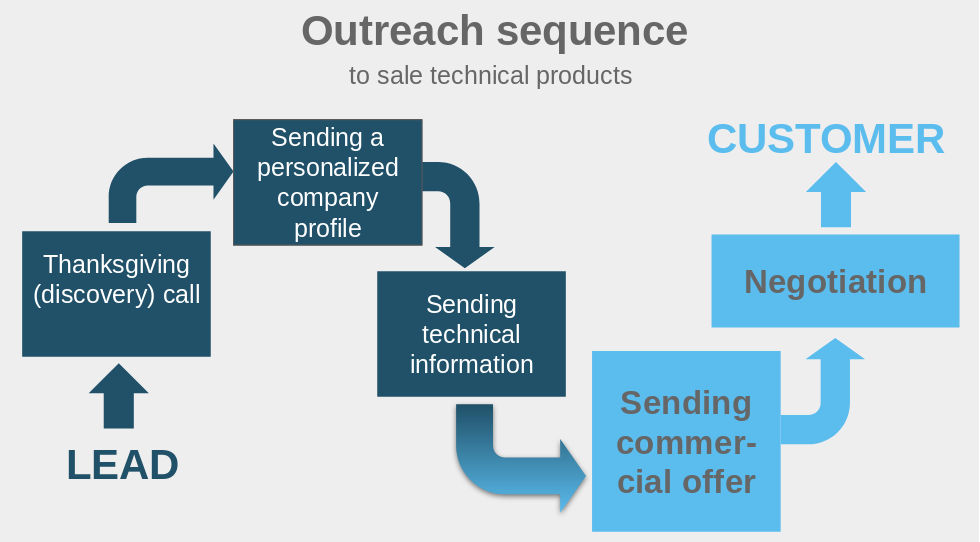
Step 1: A call is made to thank the potential customer for the interest expressed in the company’s product, trying to understand their specific interest. This phase consists of a real "discovery call".
Step 2: A brief company presentation is sent to highlight the most relevant topics for the potential customer (for example: for someone, one aspect may be the cooking speed, for another energy saving or versatility).
Step 3: During the third contact, it would be more appropriate to send technical information on machinery’s performance and application.
Step 4: If the potential customer wants to go ahead, they should be considered as "engaged" and they will probably ask for a commercial offer. At this stage, the lead is qualified to buy (sales qualified lead).
Step 5: During this call, the potential customer has most likely reviewed the commercial offer and they will want to explore some points and negotiate.
Step 6: The negotiation phase always ends with a unique result: company wins or loses a customer.
All 6 phases of the contact sequence can be managed remotely.
However, from step 5 onwards, although modern digital tools (Skype, Whatsapp, etc.) make it possible to negotiate and conclude sales effectively even remotely, the ideal would be to set up a meeting in person.
Maintaining the relationship after the sale
The third good practice, especially in cases where the sales and customer management process are exclusively managed remotely, is to keep in touch with the customer, in order to show them your availability for after-sales support.
Receiving an order is not the end but the beginning of the relationship between the customer and the company. Finding new customers is a difficult, long and very expensive process. This is why the most profitable companies have a high rate of customer retention.
Digital technologies allow to manage remotely also the after-sales phase, whose main objective is to make customers buy more and more frequently, becoming company’s ambassadors.


